
People with osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine always avoid sudden movements, carefully lean and turn to the side, slowly sit down and stand up.So they try to prevent sharp, pierced lower back pain and force them to freeze in one of the body's position.Crunch, clicks, and mobility are also disclosed.Treatment is more often conservative, but surgical intervention is required when severe damage to discs and vertebrae.
What is the lumbar spine osteochondrosis
Lumbar osteochondrosis is a degenerative-dynish pathology that initially affects intervertebral discs.Due to inadequate intake of nutrients, they lose the ability to maintain moisture.The regeneration processes slow down, the disks are flat and fragile.The distance between adjacent vertebrae decreases, so the bone tissue increases to stabilize the lumbar segment affected by osteochondrosis.Osteophytes are formed - the increase in bones, which is displaced by soft tissue structures, nerve roots, and blood vessels.
Stages of pathology
The stage of osteochondrosis is the stage of the disease, which is characterized by certain devastating changes in the vertebrae's plates and body.It is determined using an X -Gay test.The resulting images are clearly shown in the specific signs of destruction of spinal structures.Each stage corresponds to the severity of osteochondrosis, a series of symptoms.The higher the harder the disease for conservative treatment.
| Lumbar osteochondrosis stage | X -Ray features and clinical manifestations |
| First (preclinic) | X -rays do not have signs of osteochondrosis.Occasionally discomfort in the lower part after physical effort or long -term stay |
| The second | Lordosis adjustment less frequently - scenes of spinal bodies, deformation of semi -muse processes.The height of the plates is slightly reduced.Painful feelings occur more frequently, their duration increases |
| The third | Subchondral sclerosis of the closing plates, damage to a large number of half -dimensional process and a moderate decrease in the height of the plate are observed.In addition to the pain of the lumbar region, the clinic also contains crunching and stiffness of movements |
| Fourth | The half -outward and rejection are rejected.Increase in bone tissue compensation, the formation of more osteophytes.It occurs when pain and rest in pain |
The causes of illness
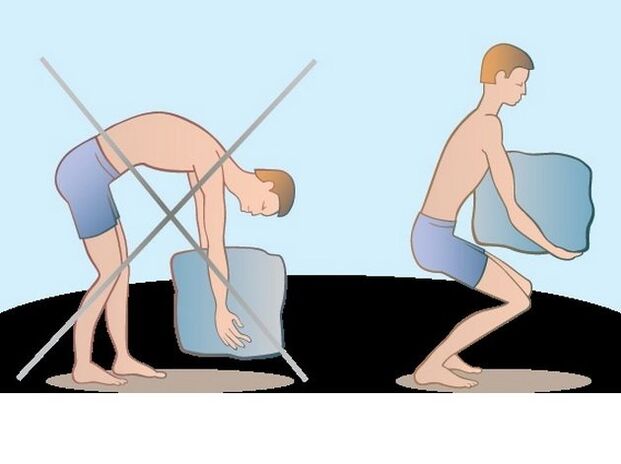
The causes of osteochondrosis are often increased loads in the lumbar spine.The plates are constantly microtrauma and have no time to recover in time.The significant part is gradually injured and starts deformation of the vertebrae bones.Such pathological conditions are also able to provoke the destruction of the lumbar segment:
- Congenital or acquired disorders - flat legs, skoliosis, kyphosis, leg deformation, TBS dyslasia;
- Systemic pathologies - rheumatoid arthritis, scleroderma, red lupus;
- endocrine and metabolic diseases- puppy, diabetes mellitus, hypo- and hyperthyroidism, obesity;
- Previous injuries - subluxation and fractures of the vertebrae, spinal damage;
- Circulatory disorders, including the background of a sedentary lifestyle.
One of the main causes of osteochondrosis is the natural aging of the body.After 50 years, recovery processes slow down, collagen production decreases, and the condition of the tapes deteriorates.
Characteristic signs and symptoms of the disease
In the early stages of development, osteochondrosis does not appear clinically.After a working day, one uses the poor pain of the muscle and does not consult a doctor.But the severity of the symptoms is slowly increasing - soon a crunching tilt and the turn of the case, sensitivity disorders and stiffness are related to pain.
Coordinated syndrome
This is the name of the defeat of the spinal roots, which leads to motor, vegetative and severe disorders.Rotor syndrome develops with 3-4 severity osteochondrosis.In these sections, a vertebral hernia is formed that squeezes the roots of the spine.The pathology is based on the type of lumbago, lumbalgia and lumbar form.In addition to severe pain, radicular syndrome is characterized by numbness, tingling, climbing goosebams, reduced or complete sensitivity.
Ischemic syndrome
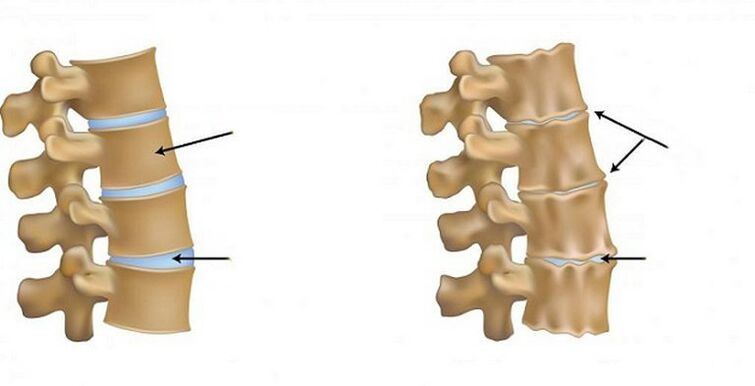
In the late stages of lumbar osteochondrosis, it may be condensing the damage to large blood vessels.The pelvic organs do not receive sufficient amounts of nutrients, which leads to a violation of their operation.The cerebral brain trophy is also nervous, neurological deficiency develops - a intermittent lameness, temperature and pain sensitivity appear.
Vertebrate syndrome
Distance between the adjacent bodies of the vertebrae and reducing the growth of bone tissue is gradually deformed by lumbar spine segments.The situation is exacerbated by the constant compensation stress of the back muscles with their later atrophy.It is pathologically altering a person's walk and posture, including improper redistribution of loads.The likelihood that other parts of the spine and the joints of the legs will be coated significantly in the devastating depressive process.
Pain syndrome
At the bottom of the back is a large sciatic nerve made up of sacred spine roots.If hernial protrusion, bone growth, cramped muscles, isias are violated - a typical symptom of lumbar osteochondrosis.Along the sitting nerve there is acute pain on the hips, knees, lower legs (lumbia).Another specific property of pathology - Lumbago or "shots" in the lower part after sharp inclination or turning, hypothermia.
Diagnostic methods
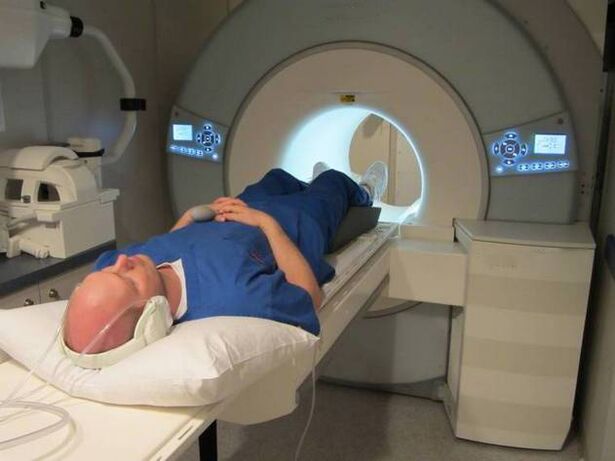
When the diagnosis is made, the two forecast radiographic images are the most informative.MRI is performed to study the lumbar segment concerned.The study allows the evaluation of the condition of the spinal cord, soft tissue structures, blood vessels, nerve roots.The degree of damage to the nerves can be determined using the potential caused, electronography, and electromiography.Discography is used to test affected discs.
How to treat treatment
They practice a comprehensive approach to lumbar osteochondrosis therapy.The purpose of the treatment is to eliminate pain, to restore the volume of movements, to prevent the spread of pathology to healthy discs and vertebrae.
Drugs
The use of non -steroid anti -inflammatory drugs, glucocorticosteroids, and muscle looser allows you to get rid of lower back pain.Medicines are used in therapy to improve blood circulation.Patients should be prescribed for Group B, Chondroprotectors vitamins.
Medical physical education
This is the most effective and affordable treatment of osteochondrosis.After treatment of physiotherapy exercises for 1-2 months a day, not only the muscles on the lower back, but also the whole back improve posture and accelerate blood supply to damaged connective tissue structures.LFK doctors recommend that patients recommend slow, smooth turns and trunks, shallow squats and lungs.
Massage
Patients with lumbar osteochondrosis show all types of massages - vacuum, acupunctural, connecting, segmental.But most of the demand is classic.During the seat, the massage therapist performs the main massage movements: caressing, rubbing, kneading, vibration.The purpose of the procedures is to eliminate muscle cramps, to improve blood circulation in the affected segment and to strengthen skeletal muscles.
Physiotherapy
During the acute and subacute period, patients are prescribed by electrophoresis or ultraphonophoresis with glucocorticosteroids, anesthesia, and group B vitamins.In the remission stage, laser therapy, magnetic therapy, stress wave therapy and UHF therapy are often performed.Ozokeritoling, paraffin applications, hirudotherapy, mud, radon, hydrogen sulfide baths are also used.
Surgical intervention
The main indication of surgical intervention is the violation of spinal cord with hernial protrusion.During surgery, the intervertebral hernia is removed and the spinal canal decompression is performed.The most commonly used methods for lumbar osteochondrosis surgical intervention are microdisctomy, puncture evaporation, or laser reconstruction of the disk, installation of implants, and stabilization of the spine segment.
Conventional medicine
After the main therapy, the results of treatment, home ointment, herbal teas, compressions, oil and alcohol are used.Folk drugs do not affect the cause of osteochondrosis and are therefore used to eliminate poor, painful pain and severity after hypothermia, sudden changes in weather conditions or increased physical activity.
The consequences of the lack of treatment
Almost all complications of lumbar osteochondrosis are provoked by the developed intervertebral hernia.Discogenous myelopathy is particularly dangerous, which does not always occur with surgery.The disorders of the pelvis, including the stool, also the urinary disorders.Osteochondrosis complications include rooster syndrome - a common cause of acute, pierced lower back pain.
Prevention and forecast measures
The prognosis is favorable in diagnosing the pathology of 1-2 degrees.Apply well for conservative treatment and it is possible in young patients to partially restore the tissues of the intervertebral discs.With the development of complications, the forecast of total healing is less favorable.
Prevention of osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine is the regulation of body weight, exclusion of overloads, and timely treatment of endocrine, metabolic diseases.Neurologists and spinals recommend visiting the swimming pool, taking part in the Akvadinavian, Scandinavian walk.



















